In this article, we discuss both latch and flip-flop are considered as the fundamental elements of the electronic system. The crucial difference between Latch and Flip-Flop is that a latch changes its output regularly according to the change in the applied input signal when it is enabled. As against in a flip flop, the output changes with input in conjunction with the clock signal. This means the clock signal acts as the control signal to display the output according to the changed input.
Latches are something in your design that always needs attention. There are tools that help designers pinpoint the existence of latches in their design as ‘must know’ information. Thus, latches and flip flops are considered as the derived sequential circuits that are used to store information. Here we will discuss all those factors which differentiate a latch from a flip-flop.
Latch:
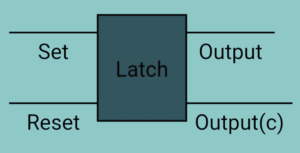
The latch is an electronic circuit, which changes its output immediately based on the applied input. It is used to store either 1 or 0 at any specified time. It consists of two inputs namely “SET” and RESET and two outputs, which are a complement each other.
Flip-Flop:
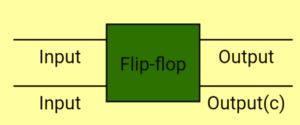
Flip-Flop is a basic digital memory circuit, which stores one bit of information. Flip flops are the fundamental blocks of most sequential circuits. It is also known as a bistable multivibrator or a binary or one-bit memory. Flip-flops are used as memory elements in sequential circuits.
Difference Between Latch and Flip-Flop
| Latch | Flip-Flop |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| For ASICs with large clock skew, latches have substantial benefits for reducing the clock period |
|
| Level-sensitive latches reduce the impact of the inaccuracy of wire load models and process variation. |
|
| In DFT, Latches needed as a lockup state at the clock domain crossings in the scan chain to avoid unpredictable behavior |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Digital Circuits Questions and Answers – Latch vs Flip-Flop MCQ:
1. Latches constructed with NOR and NAND gates tend to remain in the latched condition due to which configuration feature?
a) Low input voltages
b) Synchronous operation
c) Gate impedance
d) Cross-coupling
A) d
2. One example of the use of an S-R flip-flop is as ___________
a) Transition pulse generator
b) Racer
c) Switch debouncer
d) Astable oscillato
A) c
3. The truth table for an S-R flip-flop has how many VALID entries?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
A) c
4. When both inputs of a J-K flip-flop cycle, the output will ___________
a) Be invalid
b) Change
c) Not change
d) Toggle
A) c
5. Which of the following is correct for a gated D-type flip-flop?
a) The Q output is either SET or RESET as soon as the D input goes HIGH or LOW
b) The output complement follows the input when enabled
c) Only one of the inputs can be HIGH at a time
d) The output toggles if one of the inputs is held HIGH
A) a
6. A basic S-R flip-flop can be constructed by cross-coupling of which basic logic gates?
a) AND or OR gates
b) XOR or XNOR gates
c) NOR or NAND gates
d) AND or NOR gates
A) c
7. The logic circuits whose outputs at any instant of time depends only on the present input but also on the past outputs are called ________________
a) Combinational circuits
b) Sequential circuits
c) Latches
d) Flip-flops
A) b
8. Whose operations are more faster among the following?
a) Combinational circuits
b) Sequential circuits
c) Latches
d) Flip-flops
A) a
9. How many types of sequential circuits are?
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) 5
A) a
10. The sequential circuit is also called ___________
a) Flip-flop
b) Latch
c) Strobe
d) Adder
A) b
Related:
difference between latch and flip flop with the timing diagram
difference between latch and flip flop waveform
difference between latch and flip flop ppt
difference between latch and flip flop MCQ

