PLC Full Form
PLC stands for Programmable Logic Controller.
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a type of industrial control system that is designed to automate processes in manufacturing plants and other industrial environments. PLCs are used to control machinery, monitor production processes, and manage various other aspects of industrial operations.
PLCs consist of a processor, input, and output modules, and programming software. They are programmed using specialized software and can be customized to perform a wide range of functions. PLCs can communicate with other industrial systems, such as sensors and human-machine interfaces, to provide real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes.
What is PLC and how it works?
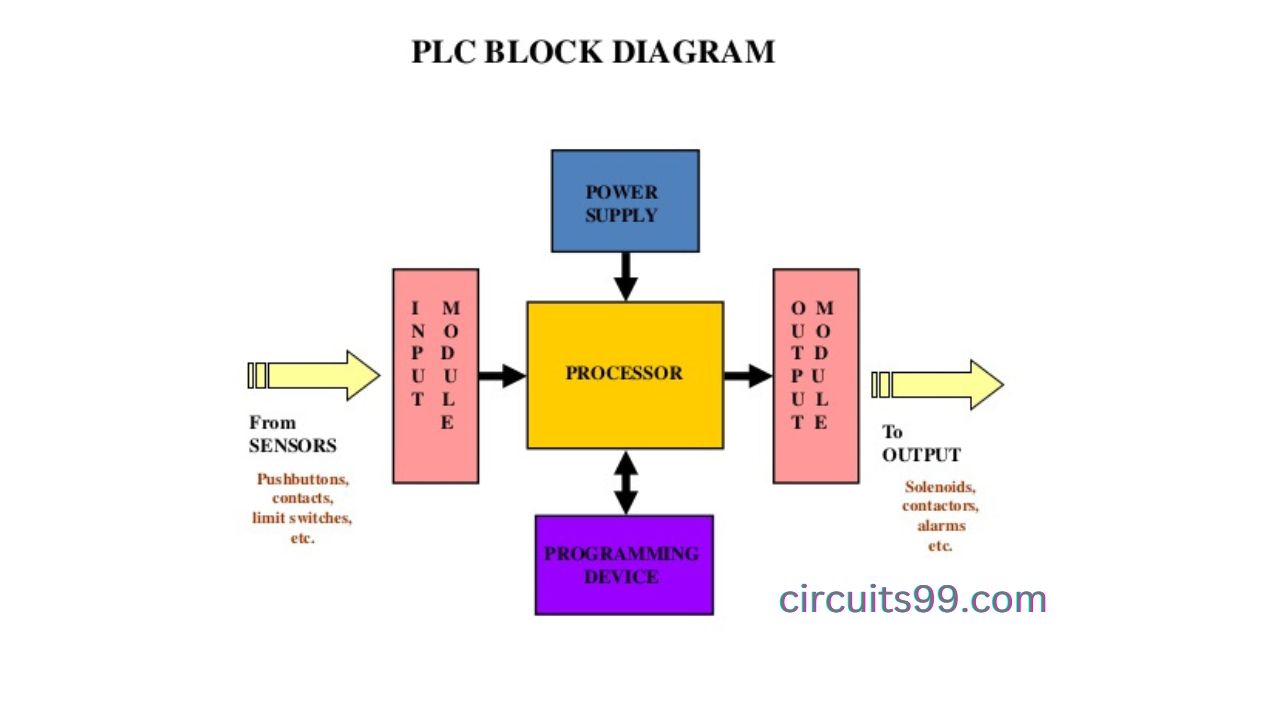
PLC stands for “Programmable Logic Controller”. It is a type of digital computer that is used to control and automate industrial processes.
PLCs are designed to be rugged and reliable, able to operate in harsh industrial environments. They are programmed using specialized software, which allows engineers to design and test control logic before it is deployed in the field.
Once programmed, a PLC operates by continually monitoring inputs from sensors and switches in the field, such as temperature sensors, pressure switches, and limit switches. It then executes the control logic programmed by the engineer, which may involve turning on or off motors, valves, or other actuators in response to the sensor inputs.
PLCs can also communicate with other devices, such as human-machine interfaces (HMIs), other PLCs, or even enterprise-level systems, to exchange data and control information. This allows for sophisticated control of complex industrial processes.
Overall, PLCs provide an efficient and flexible means of controlling and automating industrial processes and have become a critical component in many industries, including manufacturing, energy, and transportation.
What are the 3 types of PLC?
There are primarily three types of PLCs, which are:
- Modular PLCs: These are the most common type of PLCs and are designed to be customized based on the specific needs of the application. They consist of a rack or chassis that can accommodate various types of modules such as input/output (I/O) modules, communication modules, power supply modules, and others. Modular PLCs are highly versatile and can be expanded or reconfigured as needed.
- Compact PLCs: These are smaller and more cost-effective than modular PLCs, and they are designed for simpler applications that require fewer I/O points. Compact PLCs are also highly integrated, which means that they often include built-in I/O points, communication ports, and other features that are typically found in separate modules in a modular PLC.
- Rack-mounted PLCs: These are typically larger and more powerful than modular or compact PLCs, and they are designed for complex applications that require a high number of I/O points and advanced programming capabilities. Rack-mounted PLCs are often used in large industrial control systems, such as those found in oil and gas refineries, chemical plants, and other process industries.
Each type of PLC has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of PLC type will depend on the specific requirements of the application.